Ventilation (physiology)
In respiratory physiology, ventilation (or ventilation rate) is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung. It is categorized under the following definitions:
| Measurement | Symbol | Equation | Description |
| Minute ventilation | 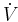 |
= tidal volume * respiratory rate[1][2] | the total volume of gas entering the lungs per minute. |
| Alveolar ventilation | 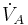 |
= (tidal volume - dead space) * respiratory rate [1] | the volume of gas per unit time that reaches the alveoli, the respiratory portions of the lungs where gas exchange occurs. |
| Dead space ventilation | 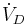 |
= dead space * respiratory rate[3] | is the volume of gas per unit time that does not reach these respiratory portions, but instead remains in the airways (trachea, bronchi, etc.). |
Contents |
Sample values
| Measure | Sample value at rest | Sample value moderate exercise[4] |
|---|---|---|
| Tidal volume | 0.5 L | 3.0 L |
| Respiratory rate | 12 breaths/minute | 30 breaths/minute |
| Minute ventilation | 6.0 L/min | 90 L/min |
| Dead space | 0.15 L | 0.15 L |
| Dead space ventilation | 1.8 L/min | 4.5 L/min |
| Alveolar ventilation | 4.2 L/min | 85.5 L/min |
Pulmonary ventilation may be evaluated using a breathing tube or spirometer, measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal walls using respiratory inductance plethysmography or by isolating the subject in an enclosed metabolic chamber.
See also
References
- ^ a b Respiratory Physiology: Ventilation
- ^ Respiratory Physiology (page 2)
- ^ Physiology at MCG 4/4ch3/s4ch3_16
- ^ Int Panis, L (2010). "Exposure to particulate matter in traffic: A comparison of cyclists and car passengers". Atmospheric Environment 44: 2263–2270. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.04.028.
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||